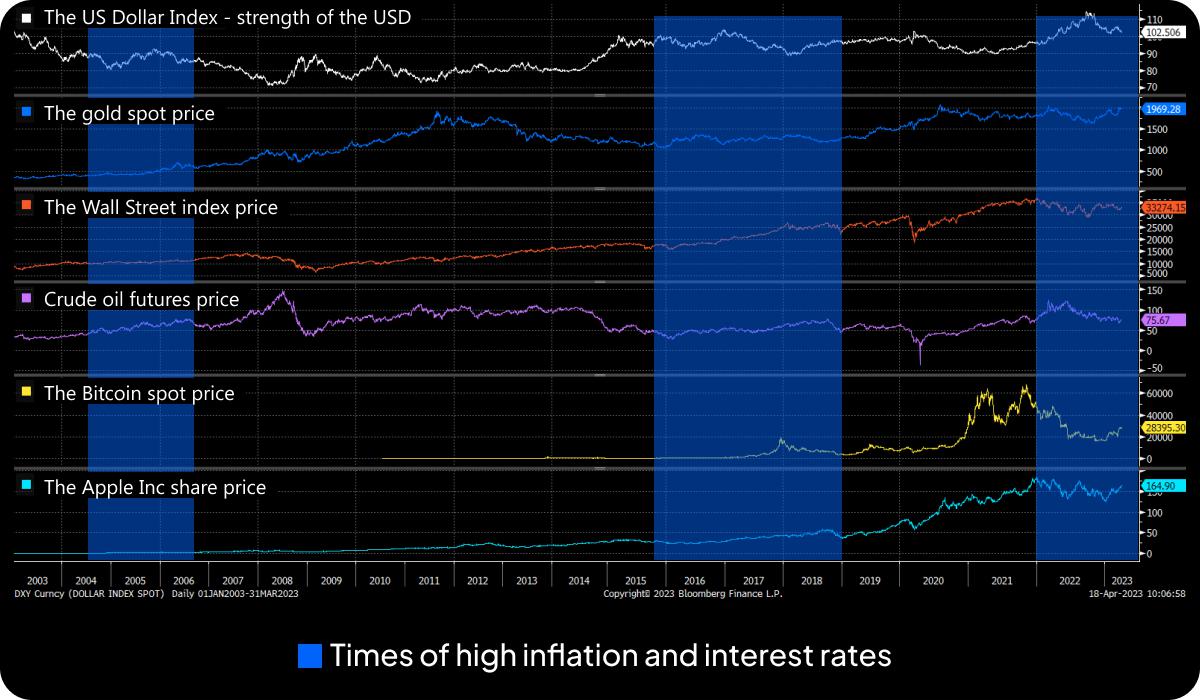
Your cheat sheet to trading during inflation and interest rate hikes

Inflation and forex
The first thing to remember about the forex market is that it’s huge, with trillions of dollars passing through the world foreign exchange market every day. So, changes in things like inflation or interest rates don’t really diminish the forex market, but rather change its rhythms and flows.
On a global level, unexpected inflation can increase volatility in the forex market, as more people speculate on what this will mean for currencies’ value. This can lead to a temporary uptick in activity on the forex market. On a national level, inflation and interest rate hikes may affect a currency’s exchange rate and competitiveness on the global stage, as things like consumer prices, infrastructure spend and big business loans become more expensive. This wouldn’t be so good for that country’s currency itself, but it wouldn’t hurt the forex market – in fact, it would likely lead to more speculation on that currency in the forex market.
If interest rates specifically increase, a country might become more globally attractive to foreign investors, because of the chance for them to earn more interest on investments there. This can lead to more demand for that currency on the foreign exchange market, causing price rises. The currency may then perform better if interest rates are raised (provided inflation isn’t elevated as well, as that could potentially detract from such returns), even potentially causing an impact on trade and the country’s economy as a whole.
This pictorial is for illustration purposes only and should not be taken as financial advice. Remember that past performance is no indicator of future results.
Pros and cons of forex trading when there’s high inflation and interest rates
- Pros: The forex market is the biggest, most liquid market in the world, and isn’t negatively impacted by things like inflation or interest rate hikes
- Pros: In fact, there are more profits and losses to be made on forex when there’s volatility – and there’s plenty during times of high inflation and interest rates
- Cons: Due to its massive size, you can accumulate significant losses very fast. Forex is also generally traded using leveraged products, which means that your losses could be larger than the margin amount you paid to open your forex trade
Inflation and stocks
Inflation and interest rate hikes affect the stock market negatively, typically. With higher operating costs (inflation) and borrowing and investing being more expensive (higher interest rates), business’ growth will often slow in these times, affecting the share price and shareholder returns. This has led to equities and the stock market generally being associated with times of economic growth, not slowdown.
Investors and traders, knowing this, will often focus less on the stock market more on asset classes more traditionally associated with uncertain times, like gold and government-linked bonds.
However, there are some stocks that can still do well during hawkish times and high inflation rates. Value stocks, which are known for steady and dependable returns in all sorts of environments, are one. Another is sellers of smaller, luxury items that consumers turn to during hard times – something called ‘the lipstick effect’.
Find out more in our article on how inflation and interest rates affect the stock market.
This pictorial is for illustration purposes only and should not be taken as financial advice. Remember that past performance is no indicator of future results.
Pros and cons of stock trading when there’s high inflation and interest rates
- Cons: Inflation and high interest rates often negatively impact many share prices and their returns.
- Cons: This often means that stocks are less popular with investors and traders during times of high inflation.
- Pros: However, certain companies, such as those known to benefit from ‘the lipstick effect’ and value stocks, are known to perform well during times of high inflation and interest rates.
- Pros: Although investors are likely to see diminished returns during inflationary and hawkish times, traders may still make profits in a negative environment, provided they short-sell when stock prices drop and go long when share prices rise. However, if they’re incorrect in their speculating and guess the wrong direction, they’ll make a loss.
- Cons: It’s important to remember that the market is unpredictable, and stocks’ past results is not a guarantee of their future performance
Inflation and commodities
The effects of inflation and rising interest rates on commodities will depend to some degree on the commodity in question. But, generally speaking, commodity prices will remain constant if demand for them remains unchanged. As a result, many investors and traders view commodities as a hedge against inflation.
If inflation leads to rising costs in producing commodities, or to a scarcity in those commodities, it will drive commodity prices up. However, it’s usually the other way around: significantly higher prices for commodities in the most constant demand – for example oil, grain and gas – will cause a rise in inflation. A good example of this is the spike in gas and grain prices in 2022 after Russia invaded Ukraine, which caused inflation worldwide.
This pictorial is for illustration purposes only and should not be taken as financial advice. Remember that past performance is no indicator of future results.
Pros and cons of commodities when there’s high inflation and interest rates
- Pros: Commodities, particularly ones that are in consistently high demand like oil and gas, tend to perform well during times of inflation and interest rate hikes
- Cons: Commodities are affected by unpredictable factors like weather patterns, countries’ politics and natural disasters more than some other asset classes, like stocks for example
- Pros: Speculating on commodities’ prices as a trader, rather than investing, can still earn a profit (or a loss) without needing to actually own them
- Cons: As with share prices (and any other market really), a commodity’s past performance – even in a very similar environment – is no indicator of future results
Inflation and gold
Although we’ve talked about commodities at large, gold deserves its own special mention because of the unique way it’s affected – or unaffected – by rising interest rates and inflation. Gold is a precious metal that is in constant demand, due to its many uses in fine jewellery, industry and investment. It’s supply, however, is finite and often limited – meaning that the price of gold is fairly constant, even during hard times.
For this reason, gold has a reputation as a safe haven asset among investors and traders, who often turn to it during uncertain times of rising economic pressure. This means that the gold price often actually goes up when inflation and interest rates are on the rise.
This pictorial is for illustration purposes only and should not be taken as financial advice. Remember that past performance is no indicator of future results.
Pros and cons of gold when there’s high inflation and interest rates
- Pros: Gold is known to be a hedge against inflation, as the precious metal generally appreciates in value in times when consumers are feeling pessimistic – often the case during inflationary periods
- Cons: Investing in gold can be an involved process, including finding somewhere secure to store your gold and obtaining the correct permissions. Not to mention that buying physical gold is generally very expensive
- Pros: Trading gold, where you’ll speculate on the gold price rather than buy actual gold outright, combines the benefits of gold as a market during inflationary times, without the hassles of owning physical gold bullion or gold coins
Inflation and indices
Surely indices are affected by inflation the same as stocks, since an index is nothing but a collection of shares? Not quite. While ‘stocks’ is the general collective term for any and every publicly traded company, an index consists of a certain basket of stocks, which are organised in a specific way (for example, weighted from biggest to smallest by market capitalisation). This index of stocks will have a certain theme, for lack of a better word, such as ‘biggest United Kingdom companies’ (the FTSE 100), ‘small cap and mid cap US stocks’ (the Russell 2000) or ‘volatility on the market’ (the VIX).
As such, this means that high inflation and interest rates will affect indices differently. For example, cost pressures from high inflation may impact the Russell 2000 index, which is made up of smaller and medium-sized companies, more than big stocks on the mighty Dow Jones index. And higher interest rate and inflation environments, which often see less investment into technology stocks, may further impact the S&P 500 index, for example, which is known to include many prominent tech stocks.
This pictorial is for illustration purposes only and should not be taken as financial advice. Remember that past performance is no indicator of future results.
Pros and cons of index trading when there’s high inflation and interest rates
- Cons: Interest rate hikes in particular are shown to negatively affect indices regarding short term performance
- Pros: However, due to their diversified nature, indices are on average proven to beat inflation and interest hikes, longer term
Inflation and cryptocurrencies
Cryptos are the newest asset class on our list, with Bitcoin only having been around since 2009. Nevertheless, economists and traders have been able to discern meaningful trends in the way cryptocurrencies respond to inflation and interest rates since then.
Cryptocurrencies are mined and distributed in their own unique way and aren’t regulated by central bankers and their monetary policies, or by countries and regions monitoring how many coins are in circulation – supply and demand factors that affect every other market’s inflation and interest level. Instead, cryptos have two kinds of ways they’re mined and produced: inflationary and deflationary. While inflationary cryptocurrencies introduce more coins over time, deflationary ones bring out less coins over time. These yield their own consequences of supply and demand and, in this way, inflationary coins (such as Bitcoin, the world’s biggest cryptocurrency) will experience their own unique form of inflation.
However, cryptocurrencies are also affected by traditional inflation and interest rate hikes. Why?
Just as foreign exchange happens in pairs, so all other asset classes are affected by what they are traded against and exchanged into. Most of the world’s more prominent cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum and Dogecoin, are purchased and redeemed against the US dollar. So, even though their worth may not be based on the USD directly, they will be directly influenced by the dollar’s performance. In fact, generalised market returns over the past several years have shown that big coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum are negatively affected by interest rates and inflation just as stock markets are.
There are even some cryptos’ valuations that are directly pegged to a currency, for example the US dollar, just like other asset classes like gold or crude oil. These are known as ‘stablecoins’, and they will directly be affected by inflation and interest rate hikes in the same way cash will.
This pictorial is for illustration purposes only and should not be taken as financial advice. Remember that past performance is no indicator of future results.
Pros and cons of cryptos when there’s high inflation and interest rates
- Cons: Bitcoin and many other older cryptocurrencies have been shown to underperform in times of high interest rates and inflation, similarly to stocks
- Pros: As an ‘alternative’ asset class not policed by central banks or tied to a formal currency, they may experience a brief and nominal uptick in popularity during inflationary, hawkish or pessimistic times as investors seek out hedges against inflation – even though cryptos’ efficacy as an inflation hedge hasn’t been proven
Related articles
Pepperstone không đại diện cho việc tài liệu được cung cấp ở đây là chính xác, hiện tại hoặc đầy đủ, và do đó không nên dựa vào nó. Thông tin, có phải từ bên thứ ba hay không, không được coi là một khuyến nghị; hoặc một đề nghị mua bán; hoặc một lời mời mua bán bất kỳ chứng khoán, sản phẩm tài chính hoặc công cụ nào; hoặc tham gia vào bất kỳ chiến lược giao dịch cụ thể nào. Nó không tính đến tình hình tài chính hoặc mục tiêu đầu tư của độc giả. Chúng tôi khuyên bất kỳ độc giả nào của nội dung này nên tìm kiếm lời khuyên của riêng mình. Mà không có sự chấp thuận của Pepperstone, việc sao chép hoặc phân phối lại thông tin này không được phép.